Table of Contents
REF: Electrical System
Electrical Concepts
Wire Gauge & Current Loads
There are many competing charts online indicating what current is allowed with various gauge wires. Maximum current ratings are to prevent the insulation on the wire from breaking down or melting due to overheating. When bundled together, the maximum rating must be reduced to account for the decrease in heat dissipation. Below is a conservative listing of the maximum current for typical wire gauges, but even these maximum ratings must be reduced under various loading conditions.
Fusing of circuits is also a concern. This quotation makes the point:
First, fuse ratings can be a bit misleading. A 10A ATO (automotive) fuse will conduct 11 amps for 100 hours minimum. At 13.5 Amps a 10A ATO fuse can take as long as 10 minutes to blow. It is not like once you draw 10 amps “poof” the fuse is gone. (From FUSE SIZING PRIMER located at http://www.powerlet.com/learningCenter/fuseSizing)
In general, for 12v wiring (13.5v source) where the length of the point-to-point runs (which equals 1/2 of the full circuit back to ground) are as follows, this rule-of-thumb chart is useful (max 3% voltage loss):
| Max Amps For PtoP Cable Run Length Of | |||
| Gauge | 3-ft | 6-ft | 9-ft |
| 18ga | 8-amps | 4-amps | 2.7-amps |
| 16ga | 13-amps | 6-amps | 4.3-amps |
| 14ga | 21-amps | 10-amps | 7-amps |
| 12ga | 30-amps | 16-amps | 11-amps |
| 10ga | 40-amps | 26-amps | 17-amps |
Also see this list of Wire Gauge By Circuit for EVO Models.
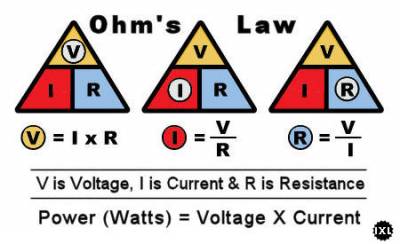
Ohm's Law For DC
The above values for DC power are: Voltage in whole Volts,
Current in whole Amps and Resistance in whole Ohms.
For many basic symbols and formulas used in electronics, go to this page,
TinkrLearnr, which has downloadable images and posters.
About Contact Resistance
- Contact resistance is the resistance to current flow (due to surface conditions and other causes) when contacts are touching one another 1)and it is the main ingredient in the electrical contact reliability.
- Electrical connections represent the weakest parts along an electrical wire chain. The main reason for these connection failures is contact resistance between the elements of connection.
- Contaminations (usually dust, found inside or outside the electric connections), films on the surfaces of contacts and increased humidity lead to an increase in corrosion, contact temperature and contact resistance of the joints. These contaminations can be due to surface oxidation, dust deposition and corrosion of contact material. The increase in contact resistance is generally attributed to corrosion film growth. So, the contact reliability is greatly degraded and contact life time is greatly reduced.
- Copper, like all other common metals, readily develops a very thin surface oxide film even at ordinary temperatures when freely exposed to air. The most widely used coating materials are tin, silver, cadmium, and nickel. Compared with uncoated copper connections the nickel and silver coating of copper connections show excellent stability and low initial contact resistance. Contact resistance between the connected joint elements causes unequal distribution of currents in the upper and lower joint parts. Therefore, there will be higher power losses at the joint ends, hence higher temperature. This higher temperature leads to an increase of the contact resistance at the joint ends.
- Contact resistance may be divided into three major components:
- Resistance of the basic metal.
- Resistance due to the converging of the lines of current flow as they pass through the small area (true conducting area) of the joint (constriction resistance).
- Resistance resulting from surface tarnish films (oxidation films), trapped between the members of the joint, frequently called as film resistance which is affected directly by the environment (temperature, humidity, vapors, dust, etc.).
- Operating and maximum temperature: The current carrying capacity of a wire connector is usually determined by the maximum temperature at which the connector is permitted to operate.
- The rate of surface oxidation in the air of conductor materials increases rapidly and may give rise in the long term to excessive local heating at joints and contacts.
- Contact clamping force: Increasing the clamping force leads to a decrease in the contact resistance.
- The continuous increasing of the clamping force improves the performance of the contact joint, but if it exceeds a certain limit, the contact spot would be damaged and so the contact resistance will be higher, i.e. a bad contact performance. This limit depends on the kind of joint material and its hardness. Generally, the life time of the contact increases by increasing the clamping force.
- A good example of clamping force gone wrong is when two wires are twisted together tightly to begin with and slowly loosen through heat and/or use which can begin the degradation of the circuit.
- Increasing the load current increases the power loss which appears as heat. Thus, the increase of the load current decreases the life time of the joints. The life time of the joints decrease with the increase of the operating temperature. 2)Connectors can “fry” because their contact resistance is too high, creating a voltage drop across them. The heat created tends to increase the resistance, and the result is more voltage drop, thus more heat.
- You cannot lower the contact resistance of two metal contacts by applying a nonconductive grease to them. 3)
Switches - AC vs DC Amperage Rating
DC Rule of Thumb - For those switches that list an AC voltage rating only, the “DC Rule of Thumb” can be applied for determining the switch's maximum DC current rating. This “rule” states the highest amperage on the switch should perform satisfactorily up to 30 volts DC. For example, a switch which is rated at 15A 125VAC (10A 250VAC), will be likely to perform satisfactorily at 15 amps up to 30 volts DC (VDC). Depending on the load, it's sometimes best not to exceed 15VDC, for these switches.
AC or alternating current is an electric current or voltage that reverses its direction of flow at regular intervals and has alternately positive and negative values, the average value of which over a period of time is zero.
DC or Direct Current is an electric current or voltage which may have pulsating characteristics, but which does not reverse direction. It's potential is always the same relative to ground, and it's polarity is either positive or negative. A battery is one example of a source of direct current.
Types of Loads
An electric load is the amount of electric power delivered or required at any specific point or points on a system. The requirement originates at the energy consuming equipment of the consumers. More simply put, a load is the piece of equipment you turn on and off.
Resistive loads primarily offer resistance to the flow of current. Examples of resistive loads include electric heaters, ranges, ovens, toasters, and irons. If the device is supposed to get hot and doesn't move, it's most likely a resistive load.
Inductive loads are usually devices that move and normally include electric magnets, like an electric motor. Examples of inductive loads include such things as power drills, electric mixers, fans, sewing machines, and vacuum cleaners. Transformers also produce inductive loads.
High Inrush loads draw a higher amount of current or amperage when first turned on, compared to the amount of current required to continue running. An example of a high inrush load is a light bulb, which may draw 20 or more times its normal operating current when first turned on. This is often referred to as lamp load. Other examples of loads that have high inrush are switching power supplies (capacitive load) and motors (inductive load).
Information from Carling switches was used as a succinct description of the basics 4).
If you would like to do further research into switch ratings, search for the Eaton (Cutler-Hammer) Switch Training Manual 5).
Other Related Topics
Electrical Tools - Multimeter, Spark Tester, Etc.